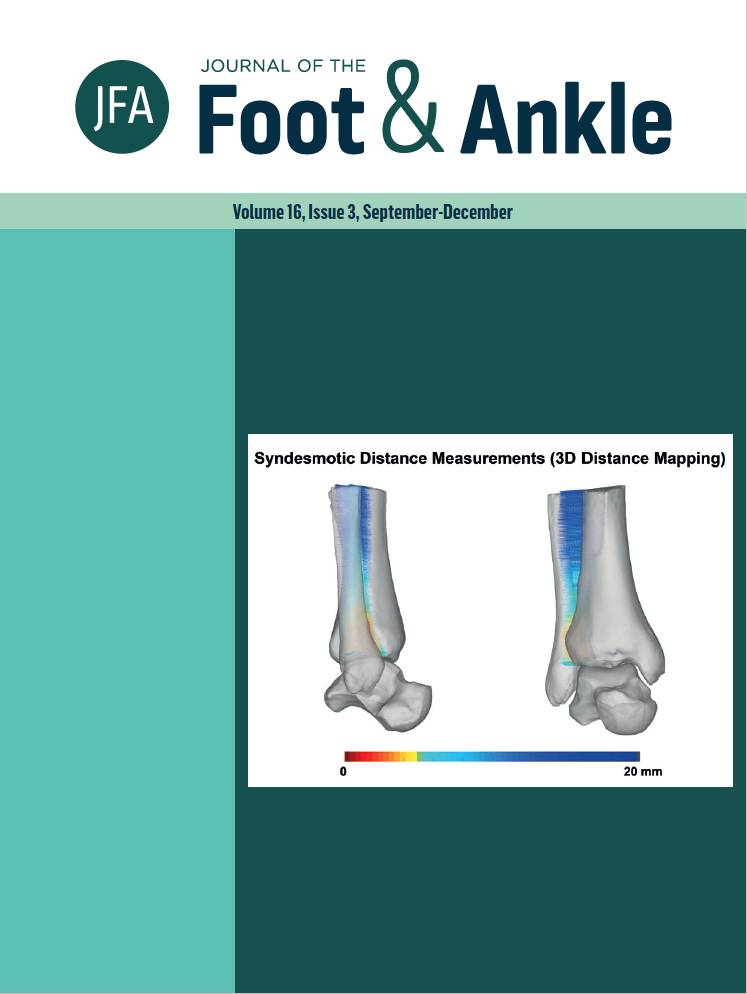
Ankle syndesmotic instability assessment using a three-dimensional distance mapping algorithm: a cadaveric pilot WBCT study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30795/jfootankle.2022.v16.1673Keywords:
Joint instability, Orthopedic procedures, Syndesmosis, Tomography, x-ray computed, Weight-bearingAbstract
Objective: This cadaveric pilot study was to develop a weight bearing computed tomography (WBCT) three-dimensional (3D) distance mapping algorithm that would allow for detection of syndesmotic instability. Methods: Pilot study, two cadaveric specimens. Syndesmotic instability was induced by release of all syndesmotic ligaments through a conventional lateral ankle approach. WBCT imaging under simulated weight bearing was acquired before and after syndesmotic destabilization. Syndesmotic incisura and ankle gutter distances were assessed using a 3D distance mapping WBCT algorithm. Results: We found increases in the overall mean syndesmotic distances in the injured syndesmosis when compared to pre-injury state, and color coded distance maps allowed easy interpretation of the syndesmotic widening following ligament sectioning and destabilization of the syndesmotic joint. Conclusion: The WBCT 3D distance mapping algorithm has the potential to allow detection of mild syndesmotic instability with a relatively ease of interpretation by using color-coded distance maps. Level of Evidence V; Cadaveric Study.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of the Foot & Ankle

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.